Drug Depot: Implantable Devices for Drug Delivery 2
Drug Depot: Implantable Devices for Drug Delivery 2
Joshua C. Doloff, Shady Farah, Atieh Sadraei, Daniel G. Anderson and Robert Langer
Koch Institute at MIT, MIT Department of Chemical Engineering, Institute of Medical Engineering and Science
Our research focuses on improved drug delivery technologies to improve biomedical treatments used in different disease models and clinical applications. In general, implanted devices and transplanted organs/tissues instigate severe rejection responses, including inflammation, immune attack, fibrosis, and scarring, resulting in loss of device function and therapeutic failure.
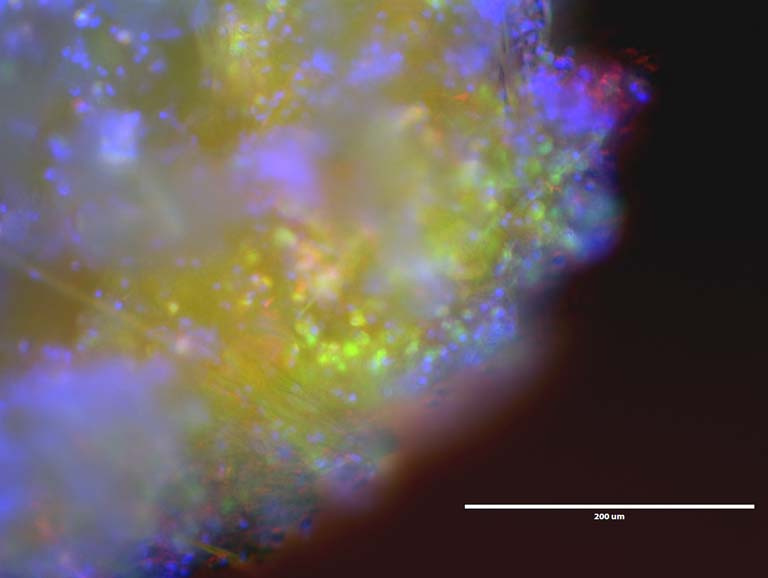
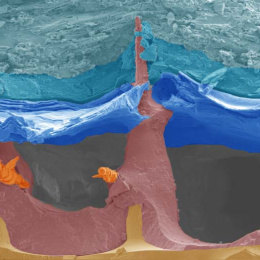
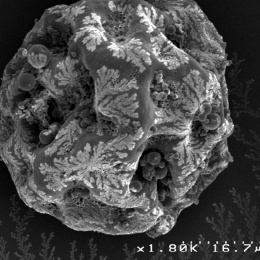
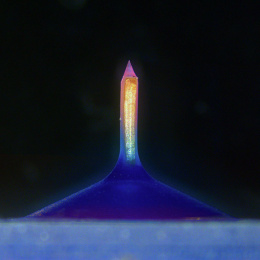
To combat these damaging responses for as long as possible, we have created crystal drug formulations to achieve long-term release, thereby eliminating the need for repeat (ie., weekly) visits to the doctor for injections. Also applicable for cancer treatments, independent of any implanted device or transplanted tissue, image 2 shows monolithic crystal drug depots, residing in fat tissue, due to their hydrophobicity, which can be applied for long-term treatment strategies