Bone Thymus-N-Harmony 1
Bone Thymus-N-Harmony 1
Emily K. Robinson
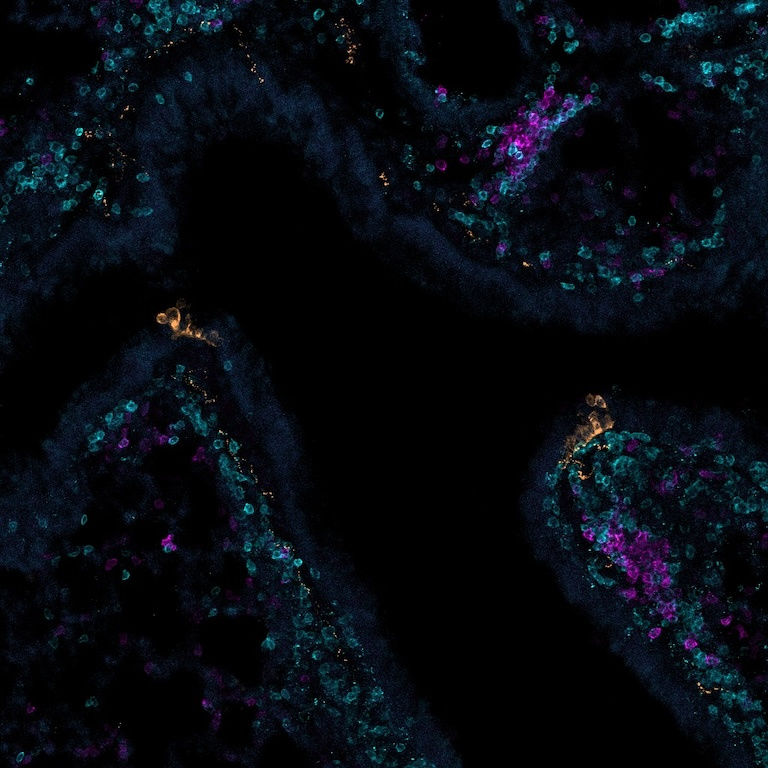
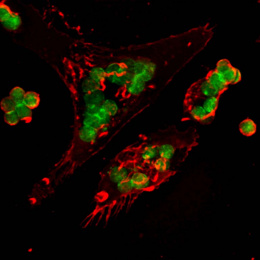
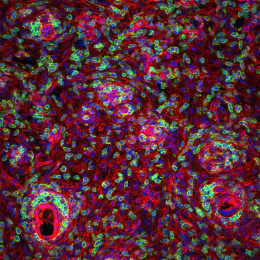
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by major inflammation in the lungs leading to breathing difficulties. In this image, we present a cross-section of the airways within asthmatic lungs, highlighting notable clumping of immune cells. Bone- and Thymus- derived immune cells (shown in magenta and light blue, respectively) tend to aggregate upon sensing irritants in the airways. They initiate antibody production as response to the detected irritants, allowing the immune system to launch an attack in efforts to safeguard the airways. However, in diseases like asthma, this immune response, intended to protect the airways, can become chronic, leading to severe respiratory issues.
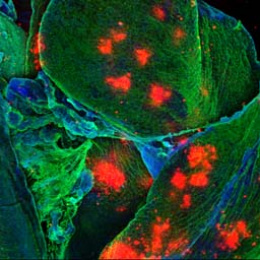
There is a very exciting clustering of immune cell beneath the pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, accompanied by substantial presence of nearby nerves in close proximity.